Chemistry Utilities 2 is comprised of the following standalone educational and scientific calculators:
Stoichiometry, Chemical Reactions, Electrochemistry and Chemical Solution.
Stoichiometry is a tool for parameterisation of chemical reactions. The application balances chemical reactions, derives molar masses, moles and actual masses of reactants and products based on their chemical formulas, stoichiometric coefficients and any quantitative data provided. Thus, it is enough to provide initial or final (after reaction accomplishment) mass or moles of one of the reaction component, to calculate all required and obtained masses and moles of all components. If data is available for several components, then limiting reagent will be found based on reaction stoichiometry.
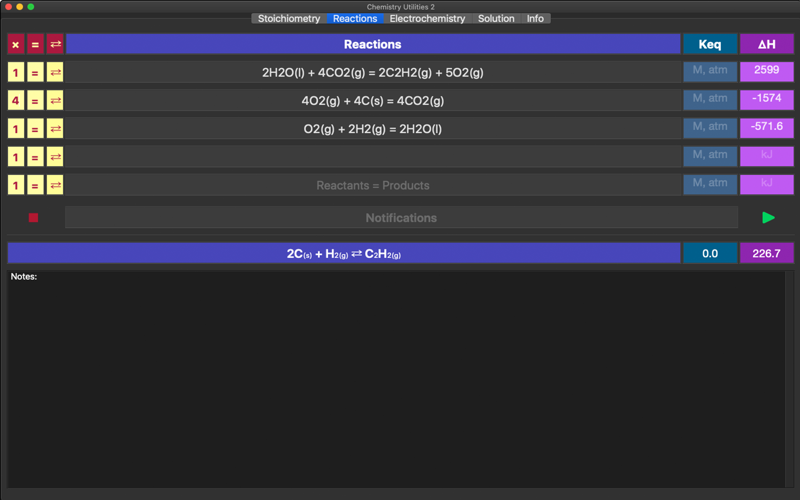
Chemical Reactions is a tool for manipulation with multiple chemical reactions. Have you ever wondered what happens to chemical reaction equilibrium constant and enthalpy when reactions are added, reversed or multiplied by constant? This app will help to investigate the complex reaction mechanisms and calculate the multistep process thermodynamic parameters, such as enthalpy (heat release/absorption) and equilibrium constants.
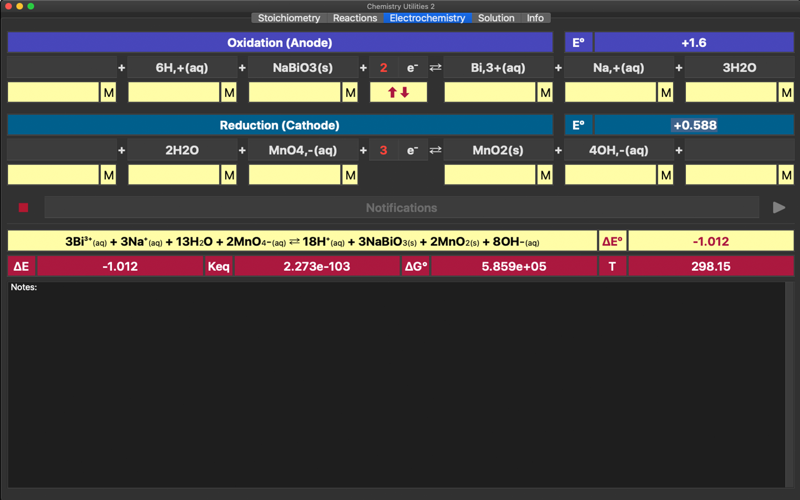
Electrochemistry is a tool for parameterisation of oxidation-reduction reactions and electrochemical cells. The app helps to equilibrate and combine the standard half-reactions into a single redox equation and to find the overall standard potential, equilibrium constant, standard free Gibbs energy and total voltage. The app is based on Nernst equation. The application includes redox reactions database. Upon typing into the leftmost field of any of a half reactions, list of the suggested equations will appear.
Chemical Solution helps in preparation of simple chemical solution by dissolution of solid solute and in finding of moles, Molar masses and required weights of compounds.
Important points, concerning chemical formula :
Charge, if exist must be provided as well, separated by coma: Na,+ .
Application supports state indexes: (g), (s), (l), (aq) – all are lowercased only, placed at the end of compound formula: OH,-(aq), C6H12O6(aq). Its considered to be a crucial part of a molecule, so same molecules of different states appearing on the opposite sides of equation are not cancelled!